Let us know first what atmospheric pressure is? Air has mass and due to that mass it exerts pressure on the earth surface. This is called atmospheric pressure. The greater the mass of air above earth surface, the higher the pressure, and vice-versa.Therefore air pressure at sea level is more and falls with increasing attudite. The standard atmospheric pressure at sea level is 14.7 pounds per square inch. Atmospheric pressure and winds are closely related to each other and affect the earth’s weather and climate.
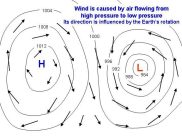
When air becomes warm it rises, leaving low pressure on earth and is replaced by cold air to equalize the difference. Therefore air always moves from high pressure to low pressure areas to equalize the difference in pressure, which is what we call as Wind.
Coriolis force
Once air has been set in motion by the pressure difference, it undergoes an apparent deflection from its path. This apparent deflection due to earth rotation ,which is called the “Coriolis force”.
In the northern hemisphere, air moving from high pressure to low pressure is deflected to the right by the Coriolis force. In the southern hemisphere, air moving from high to low pressure is deflected to the left by the Coriolis force. Note, that hot areas have low and cool areas have high air pressure because the sunlight falls directly on it and its air becomes hot and rises up leaving low pressure and in cool areas the air is denser and remains on the surface. Air blows from high pressure areas to low to compensate for the pressure.
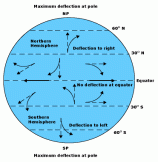
The amount of deflection the air makes is directly related to both the speed at which the air is moving and its latitude. Therefore, slowly blowing winds will be deflected only a small amount, while stronger winds will be deflected more. Likewise, winds blowing closer to the poles will be deflected more than winds at the same speed closer to the equator. The Coriolis force is zero right at the equator.
The closer the high and low pressure areas, the stronger the winds will be. The greater the difference in pressure, the higher the wind speed will be.
What are the trade winds?

The trade winds blow in the same direction throughout the year i.e., from northeast in the northern hemisphere or southeast in the south hemisphere to the equator.The Coriolis Effect makes the trade winds bend to the west, whether they are traveling to the equator from the north or south. The reason for the blow of the trade wind to the equator is that the equator is hot because of (direct sunlight) and with less air pressure and tropical latitude is cold (no direct sunlight) with high air pressure. wind blows from high pressure to low pressure areas. Trade winds blew from east to west therefore when traders in ships wanted to go westward they became dependent on it.
Small scale winds
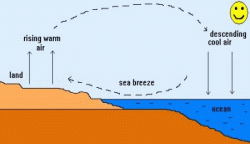
Sea breeze
During the day time the land heats up faster than the sea. As a result the air above land becomes warmer, lighter and it rises up and creates low pressure over the land. The cooler, denser air over the sea with high pressure moves towards the land to replace the warm air and equalize the pressure difference resulting in a sea breeze. The sea breeze offers a pleasant cooling effect on a hot summer afternoon.
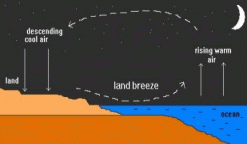
Land breeze
Land breeze occurs at night when the land cools faster than the sea. During night time the air above the sea is warmer than air above the land,so air moves from the land to the sea.
What is a monsoon?
A monsoon is a seasonal wind, found especially in Asia. In the summer, a high pressure area lies over the Indian Ocean while a low pressure exists over the Asian continent. The air masses move from the high pressure over the ocean to the low pressure area over the continent, bringing moisture-laden air to south Asia accompanied with heavy rain. During winter, the process is reversed.

Two factors are necessary to specify wind: Speed and Direction.
Zia Ahmed Khan, e-mail: khanziaahmrd50@gmail.com
xxxxx
.